Plastics sorting and recycling in France
While the French roadmap for circular economy sets the ambitious target of 100% recycled plastics by 2025, packaging ecodesign remains a key stake. The COTREP supports actors willing to improve the recyclability of their plastic packaging from the design stage. Essential stages to reach this target include also waste sorting at home and in sorting facilities furthered by the actual packaging recycling.
Step 1: household waste sorting
Since 1992, French people can sort part of their packaging separately: paper-cartons packaging, metal packaging, but also plastic bottles.
Since 2012, with the project of extension of the sorting instructions, more and more French can now sort pots, trays, as well as plastic films.
By 2019, 23 million French people were covered by this extension and could sort all their packaging. Since 2023, all French people have been able to do so.
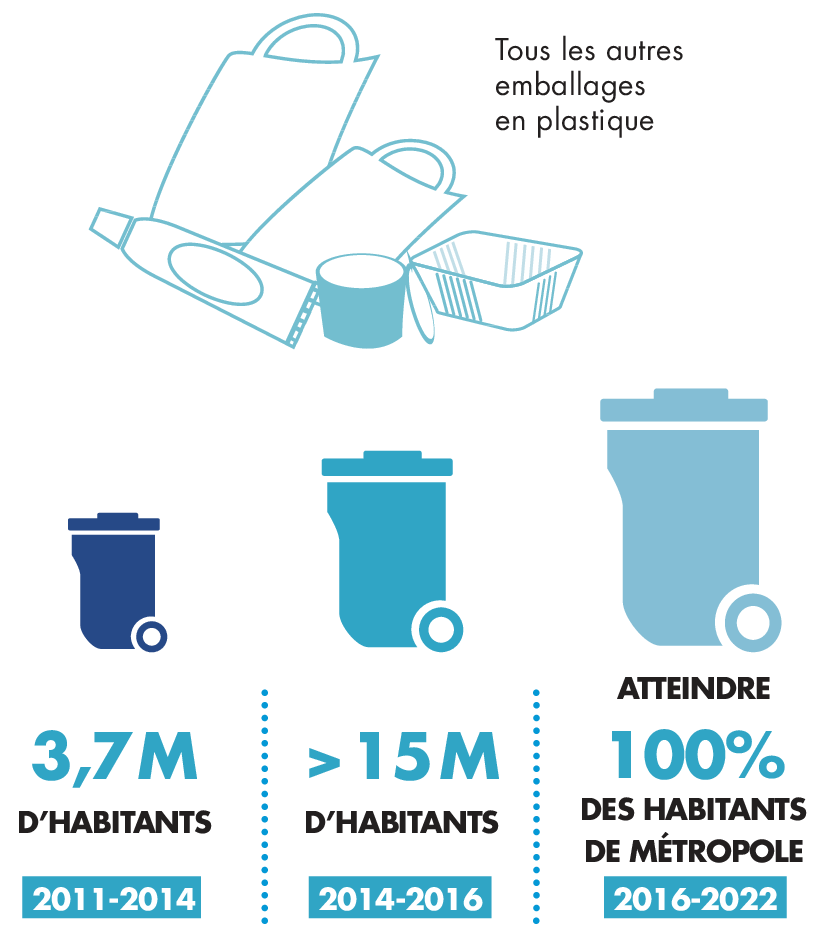
Implementation of the extension of the sorting instructions on the French territory. Source: CITEO.
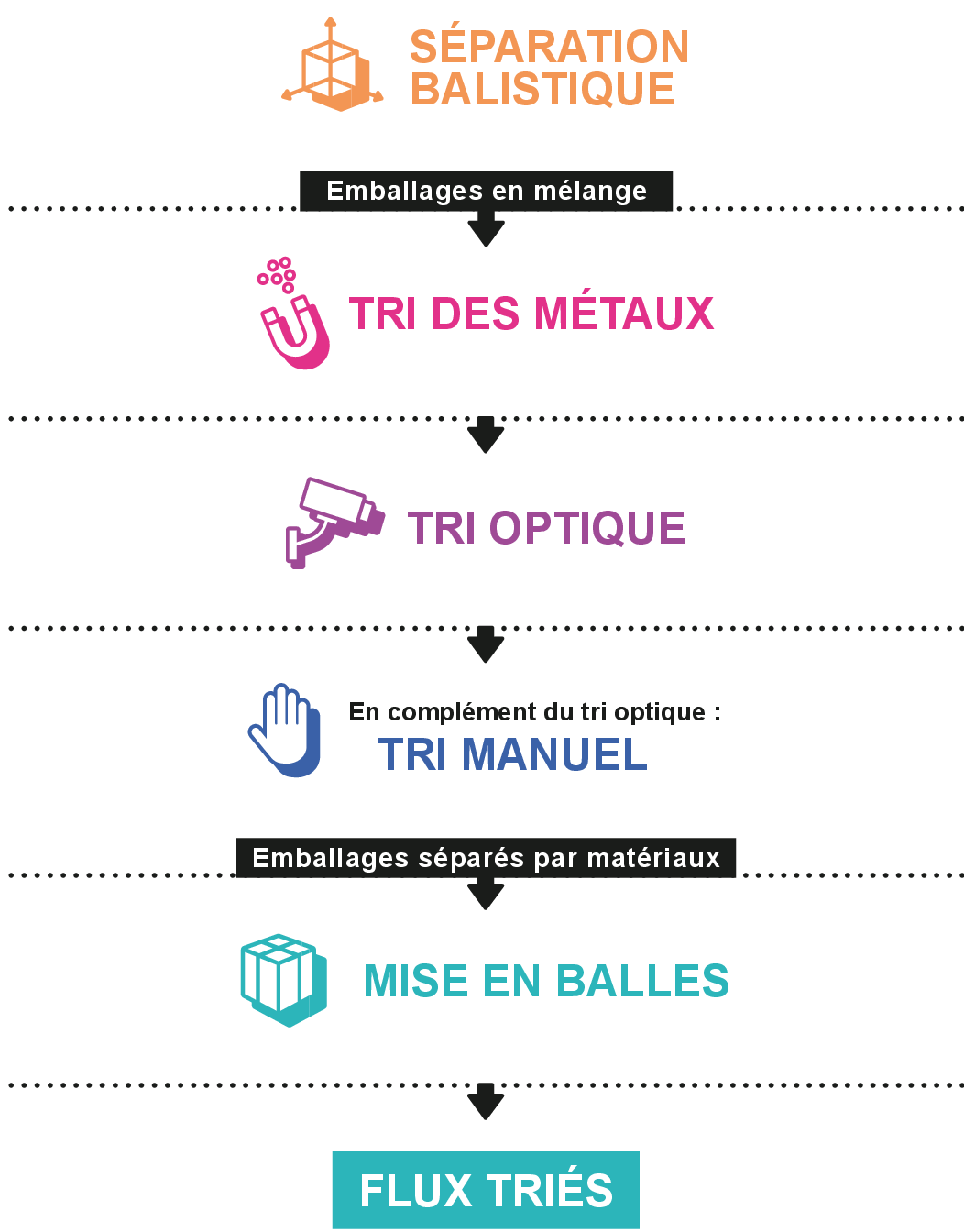
General sorting process in sorting facilities. Source: COTREP
Step 2: sorting in sorting facilities
In France, household waste packaging is sorted in nearly 200 sorting facilites (2019 data) according to their material. Several stages take place in the sorting centers:
– Ballistic separation: packaging is separated according to their shape and size. In this step, packaging with a small size or volume are less extracted (e.g. pods and bottles <20ml or films with size <size A5).
– Metals separation: plastic packaging containing metallic elements (steel or aluminum) can be oriented with plastics or metals according to the quantities of metal and depending on the machine settings (for example: PET jars with a steel hinge or mixed aluminum cans /plastic)
– Optical sorting: with infra-red sorting technologies, plastics can be separated by resin (PET, HDPE, PP, etc.). Some elements may interfere and reduce the efficiency of optical sorting: sleeves made of a material that is different from packaging body, complex trays made of several plastic resins, black packaging, etc.
– Manual sorting: the human eye is still essential to ensure a good quality of materials sorted out of sorting centers.
– Baling: the sorted materials are compacted and baled, then shipped to the regenerators.
The separation of materials is based on the regenerators and their interest in the different materials and types of packaging with regard to the final applications envisaged.
To date, bottles (PET, HDPE and PP) are sorted in French sorting centers. In region with extended sorted instruction, additional plastic packaging are sorted: mono-PET, mono-PE, mono-PP pots and trays, PS pots, and mono-PE films.
Step 3: mechanical recycling
Some regenerators are specialised in PET recycling while others in HDPE, PP, and sometimes PE films recycling. From the bales of materials they receive, they produce recycled material through several stages:
– Opening of bales: packaging bales are opened and packaging item are unpacked.
– Optical & metals sorting: as in sorting centers, plastic regenerators are equipped with optical sorters and metal detectors to perform new sorting operations and eliminate unwanted materials.
– Shredding: packaging is then shred into flakes of about one centimeter. The presence of elements other than plastic (glass beads, metal element) can damage equipment.
– Washing: the flakes are washed. Depending on the ink, pigment or glue used, some particles can disturb the regeneration or pollute the washing water.
– Flotation: flakes are separated according to their density, those with a density greater than 1 sink while those with a density less than 1 float. At a PET regenerator, the sinking material is of interest (PET density> 1), while at polyolefin regenerator, the floating flakes are of interest (PE or PP density <1).
– Optical sorting of flakes: some regenerators are equipped with optical sorting equipment that allows to sort the flakes according to their material and color.
– Extrusion / Granulation: some regenerators can perform an extrusion / granulation step which consists of heating the flakes together. The melt thus produced then passes through a die to produce spaghetti which is cut into small pieces. These are called plastic pellets and can be directly used in plastics processes.
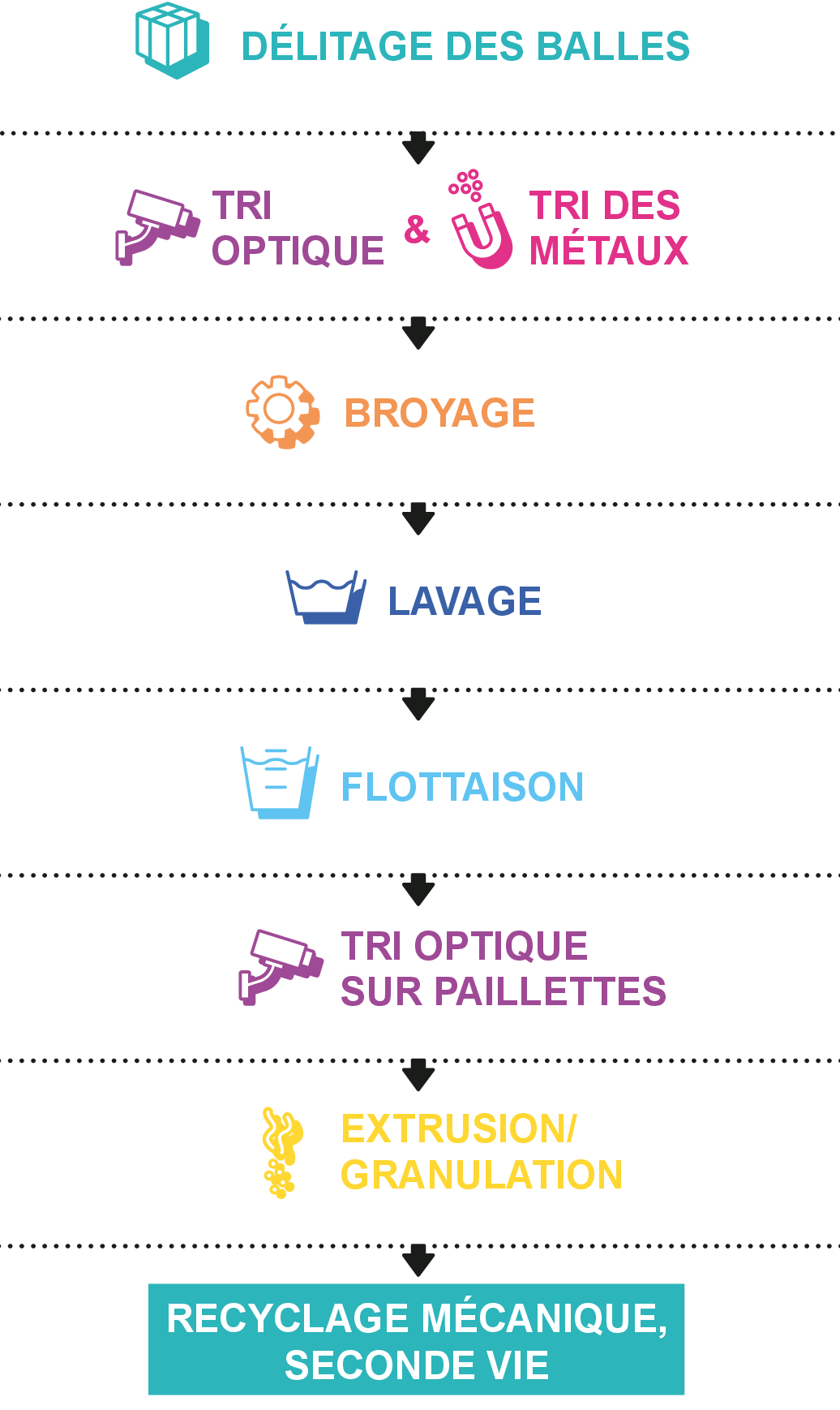
General process of plastic regeneration. Source: COTREP
The recycled material is then reincorporated into new products.
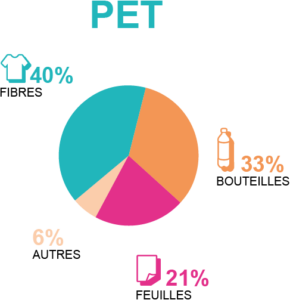
2017 PET regeneration outlets in France. Source: Valorplast
Step 4: the use of recycled material into new products
Today, PET, HDPE and PP have found their outlets. The applications of recycled PET, PE and PP vary depending on the mechanical characteristics, colors or quantities available of the recycled material.
PET packaging is recycled into textile fibers, bottles or sheets to make new trays. In France, PET is the only plastic material that can be decontaminated during the regeneration process and can be reused in food contact packaging.
HDPE and PP packaging, when recycled together, is currently used to make pipe or mandrels. When PP is recycled alone, it can for example be used in automobile parts.
Flexible PE packaging is mainly recycled into garbage bags and irrigation pipes.
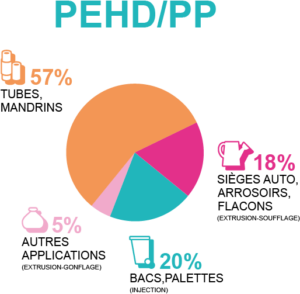
2017 rigid HDPE/PP packaging recycling outlets in France. Source: Valorplast
With France’s circular economy roadmap and the extension of sorting guidelines to all packaging, new outlets will be developed to increase the use of recycled materials in packaging and in new products.
